Losing teeth can be a nightmare for anyone, and the thought of having loose teeth is enough to send shivers down our spines. While we may take good care of our pearly whites by brushing regularly and flossing daily, sometimes gum disease can creep up on us without warning. Gum disease is one of the leading causes of tooth loss in adults, but it doesn’t have to be that way! In this blog post, we will explore how gum disease treatment could be the key step you need to save your loose teeth from falling out for good! So buckle up and let’s dive into this essential topic!
What is Gum Disease?
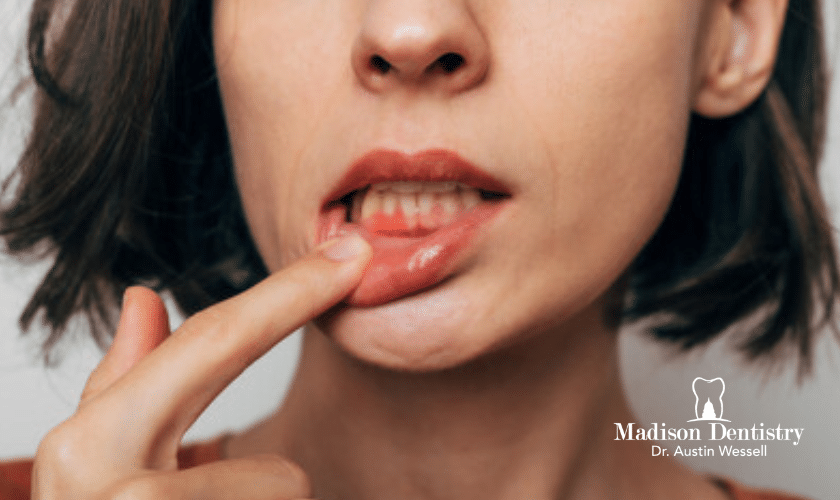
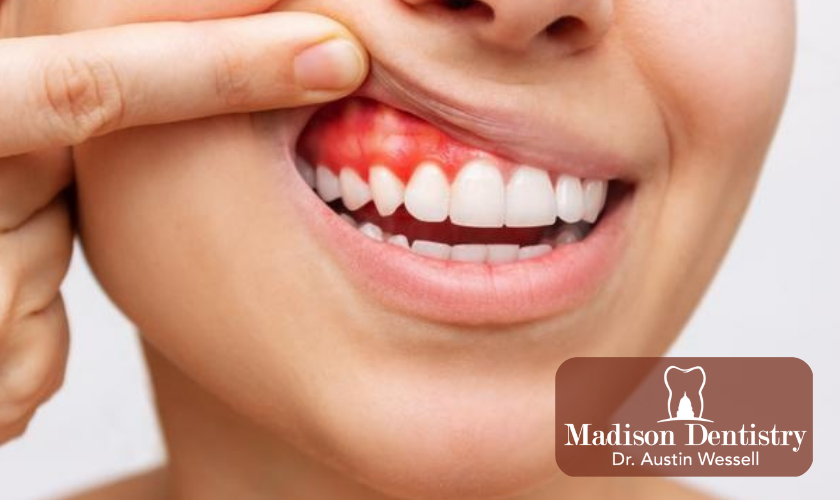
Gum disease is a progressive condition that affects the tissues and bones that support your teeth. If you have gum disease, your gums may bleed when you brush or floss. You may also have red, swollen, or tender gums. Gum disease can lead to the loss of teeth.
Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease. It usually doesn’t cause pain or damage to your teeth. But it’s important to treat gingivitis because it can progress to periodontitis, a more serious form of gum disease. Periodontitis can cause tooth loss if it’s not treated.
Treating gum disease starts with good oral hygiene at home and regular dental checkups and cleanings. Your dentist may also recommend special treatments to control gum disease.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
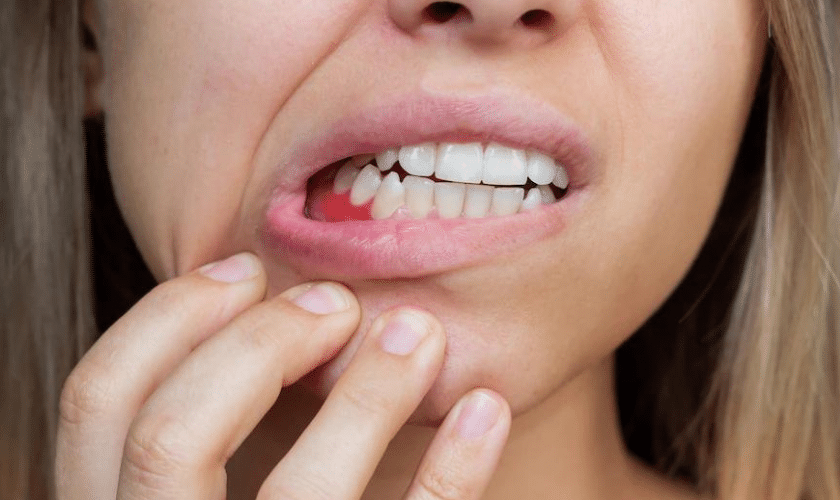
Gum disease is a serious infection of the gums that can lead to tooth loss. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of gum disease so that you can seek treatment as soon as possible.
The most common symptom of gum disease is bleeding gums. This can occur when you brush your teeth or floss. Other symptoms include:
-Red, swollen, or tender gums
-Gums that pull away from your teeth
-Pus between your teeth and gums
-Persistent bad breath
-A change in the fit of your dentures
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a dentist right away. If left untreated, gum disease can destroy the tissues and bone that support your teeth. In severe cases, it can lead to tooth loss.
Causes of Gum Disease
The causes of gum disease are numerous, but they can broadly be classified into two categories: plaque-related and non-plaque-related. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that constantly forms on our teeth. If not removed, it can harden and turn into tartar, which is much more difficult to remove. Plaque and tartar buildup can irritate the gums, causing them to become red, swollen, and tender. This is the first stage of gum disease, called gingivitis. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more serious form of gum disease. Periodontitis occurs when the plaque and tartar below the gum line begin to break down the bone and connective tissue that support the teeth. This can eventually lead to tooth loss.
Non-plaque-related causes of gum disease include hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy), certain medications (such as those used to treat high blood pressure or heart conditions), genetic predisposition, and underlying health conditions (such as diabetes).
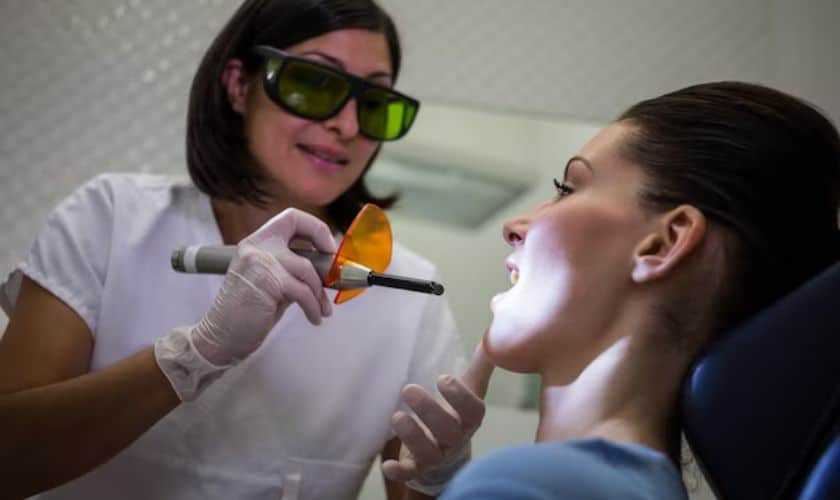
Treatment Options for Gum Disease
If you have gum disease, also called periodontal disease, there are a number of treatment options available to you. The first step in treating gum disease is to visit your dentist or periodontist for a consultation. They will evaluate the severity of your gum disease and develop a treatment plan based on the specific needs of your mouth.
The most common treatments for gum disease include:
Scaling and Root Planing:
This is a deep cleaning procedure that removes tartar, plaque, and bacteria from below the gum line. It’s often the first line of defense against gum disease.
Antibacterial Mouthwashes and Toothpastes:
These products can help reduce plaque and bacteria in the mouth, which can lead to gum disease.
Oral Antibiotics:
These medications can help kill bacteria that contribute to gum disease. They are typically used as a short-term treatment option.
Surgery:
In more severe cases of gum disease, surgery may be necessary to remove diseased tissue or repair damage caused by the disease.
How to Prevent Gum Disease
Gum disease, also called periodontal disease, is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth. It’s usually caused by plaque, a sticky film of food debris, bacteria, and saliva. If plaque isn’t removed, it can harden and turn into tartar. Tartar irritates your gums and promotes inflammation. Left untreated, gum disease can destroy the tissue that supports your teeth and eventually lead to tooth loss.
Fortunately, gum disease is largely preventable. The best way to prevent gum disease is to brush twice a day, floss daily, eat a balanced diet, and see your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups. Below are some specific tips for preventing gum disease:
– Brush your teeth twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush. Be sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, top, and sides. Use gentle circular motions rather than vigorous scrubbing.
– Floss daily using an interdental brush or floss threader to get between all of your teeth. Be sure to use gentle motions so you don’t damage your gums.
– Eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid sugary snacks and drinks as well as tobacco products.
– See your dentist regularly for professional cleanings and checkups at least twice a year (or more often if you have periodont
The Connection Between Loose Teeth and Gum Disease
Gum disease is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth. It’s usually caused by plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that constantly forms on your teeth. If plaque isn’t removed, it hardens into tartar (calculus). Both plaque and tartar irritate and inflame your gums.
If gum disease progresses, it can destroy the gum tissue and even the bone that supports your teeth. This eventually leads to tooth loss.
Gum disease is a major cause of loose teeth. In fact, loose teeth are often one of the first signs of periodontitis, a more advanced form of gum disease. Periodontitis occurs when the gums pull away from the teeth and form pockets. These pockets become filled with bacteria and pus. The bones and connective tissues that support the teeth are gradually destroyed. As the condition progresses, the teeth may become loose and eventually fall out.
Gum disease is highly preventable with regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene habits at home. However, if you already have gum disease, it’s important to see a dentist or periodontist for treatment. Treating gum disease can help save your existing teeth from being lost to periodontitis.
Treatment Options for Loose Teeth
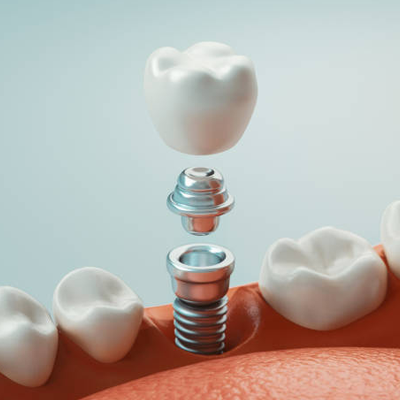
There are a number of different treatment options available for patients with loose teeth, depending on the severity of their condition. For patients with mild gum disease, a simple scaling and root planing procedure may be all that is necessary to clean out the infected areas and improve gum health. More advanced cases of gum disease may require more aggressive treatments such as periodontal surgery or tooth extractions. In some cases, dental implants may be used to replace any teeth that have been lost due to periodontal disease.
No matter what treatment option is right for you, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible if you think you may have gum disease. Early intervention can help prevent the condition from progressing and causing further damage to your teeth and gums.
Conclusion
Gum disease treatment is essential for saving loose teeth. With proper prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of gum disease, you can keep your teeth healthy and strong for many years to come. If you have been diagnosed with periodontal disease or suspect that you may be at risk, it’s important to speak with a qualified dental professional as soon as possible in order to get started on the appropriate course of action. Taking the necessary steps now will ensure that your smile stays beautiful and strong throughout your life.
FAQs:
Answer: Look out for these symptoms: persistent bad breath, red or swollen gums, bleeding gums, receding gums, and loose teeth. If you experience any of these, please see a dentist right away.
Answer: In the early stages, gum disease is reversible with good oral hygiene habits and professional dental cleanings. However, once the disease progresses to more advanced stages, it becomes much more difficult to treat.
Answer: Gum disease is the leading cause of tooth loss in adults. Additionally, research has linked gum disease to other serious health conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes.